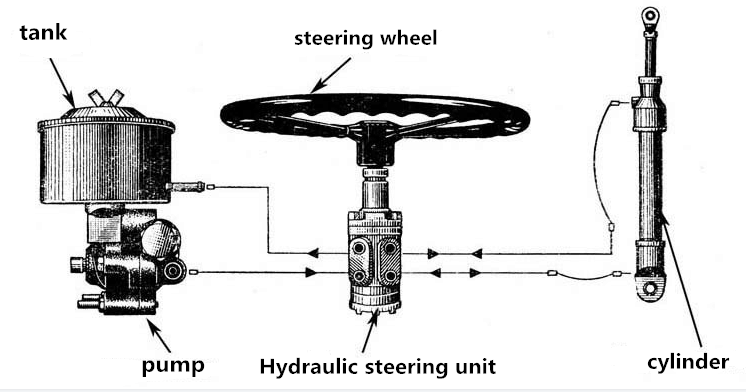
- Structure of hydraulic steering unit

Structure introduction: The composition of the rack and pinion power steering unit is composed of three parts: control valve, mechanical steering unit and booster cylinder. The control valve is a rotary valve with advanced structure, high sensitivity, and widely used abroad.
The mechanical steering unit is a rack and pinion type. The following are respectively introduced:
(1) Control valve: a normally open rotary valve composed of torsion rod 1, input shaft 2, valve sleeve 3, and other parts. The hydraulic oil is input into the left and right oil chambers through the pre-opening gap between the input shaft 2 and the valve sleeve 3.
(2) Mechanical steering part: It is a rack and pinion type, consisting of three parts: a gear shaft, a rack piston assembly and a steering rod. The booster cylinder is a metal shell, and the internal rack piston divides it into two left and right oil chambers, which are respectively connected with the two oil ports of the control valve.
Middle position:
When the car is driving straight (the steering wheel is not moving), the oil pump supplies hydraulic oil from the oil inlet. After the pre-opening gap of the rotary valve, because the rotary valve does not move at this time, the hydraulic oil flows from the oil return port to the Oil tank, at this time, the same oil pressure in the two working chambers of the steering unit does not produce power assistance.
Steering process:
When the steering wheel is turned, the gap of the valve groove between the valve sleeve and the input shaft is changed, so that the hydraulic oil flowing to the two working chambers forms an oil pressure difference. The oil pressure difference acts on the piston to push the piston to overcome the steering resistance and produce displacement, thereby driving the steering rod assembly to move to achieve power steering.
Return process:
After the steering is completed, the force on the steering wheel disappears. Due to the elastic force of the torsion bar, the input shaft returns to the equilibrium position relative to the valve sleeve, and the oil pressure difference between the two working oil chambers of the steering gear follows. After disappearing, under the action of the automatic torque of the front wheels of the car, the car will move to the straight driving position until it returns to the straight driving position.
Road sensation effect:
Road sensation effect is the ability to produce steering sensation. When the driver exerts force on the steering wheel, it also acts on the torsion bar of the steering gear and causes it to twist and deform. The amount of deformation depends on the steering resistance of the wheels; when the steering resistance increases, the amount of deformation also increases. Therefore, the driver can judge the change of the steering resistance according to the force he adds to the steering wheel to obtain the "road feel" effect.
- Previous article: What are the components of a hydraulic motor

 中文
中文 English
English Español
Español Français
Français